Angle Bisector Theorem Definition
Awasome Angle Bisector Theorem Definition Ideas. The angle bisector in geometry is the ray, line, or segment which divides a given angle into two equal parts. That line that was used to cut the angle in half is.
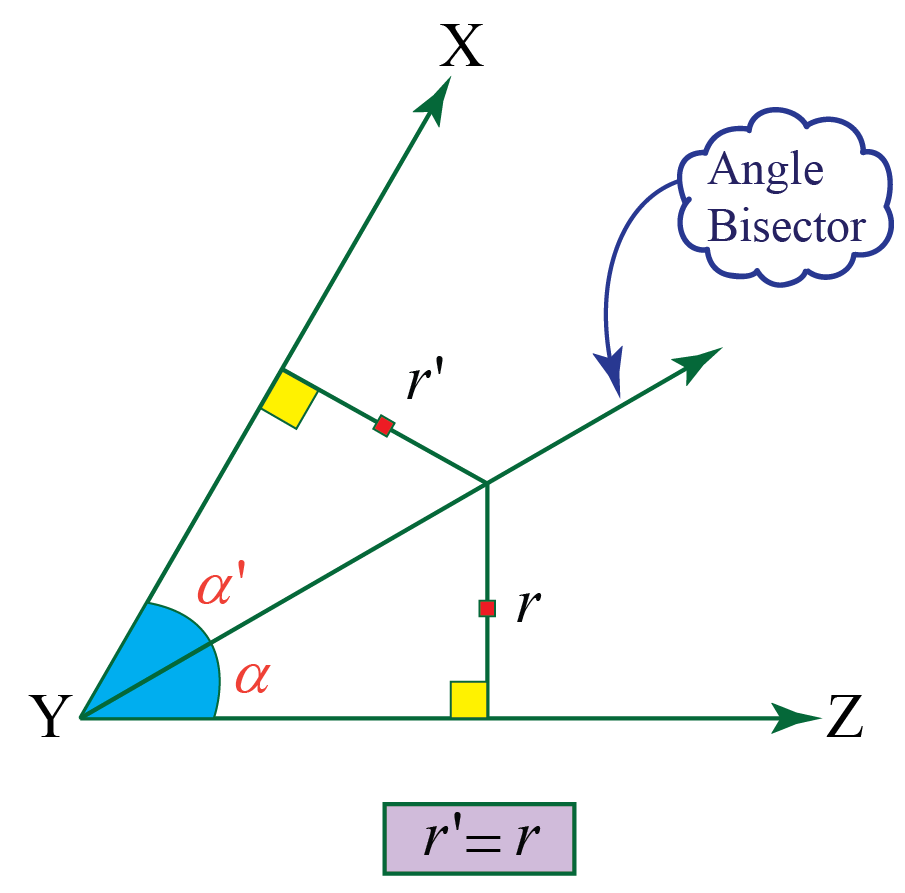
As you can see in the picture below, the angle bisector theorem states that the angle bisector, like segment ad in the picture below, divides. The angle bisector equidistant theorem states that any point that is on the angle bisector is an equal distance (equidistant) from the two sides of the angle. According to the angle bisector.
So It Tells Us That The Ratio Of Ab To Ad Is Going To.
In above figure bd is bisect the ∠abc. An immediate consequence of the theorem. If a straight line through one vertex of a triangle divides the opposite side internally (externally) in the ratio of the other two sides, then the line.
The Angle Bisector Equidistant Theorem States That Any Point That Is On The Angle Bisector Is An Equal Distance (Equidistant) From The Two Sides Of The Angle.
(bisect means to divide into two equal parts.) try moving the points below, the red line is the angle bisector: It can be used in a calculation or in a proof. As you can see in the picture below, the angle bisector theorem states that the angle bisector, like segment ad in the picture below, divides.
The Angle Bisector Theorem Is Commonly Used When The Angle Bisectors And Side Lengths Are Known.
The angle bisector theorem states that an angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side of the given triangle into two parts such that they are proportional to the other. A line that splits an angle into two equal angles. In ∠abc, bd is angle bisector of ∠abc.
The Angle Bisector Theorem States That If There Is A Triangle, And An Angle Bisector Is Created On One Of The Angles, The Line Segment Across From That Angle Will Be Segmented.
Now picture one of the triangle',s angles being split into two equal smaller triangles. In geometry, the angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle',s side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. Angle bisector of any angle will divide the opposite side in the ratio of the sides containing the angle.
The Angle Bisector Theorem Says That An Angle Bisector Of A Triangle Will Divide The Opposite Side Into Two Segments That Are Proportional To The Other Two Sides Of The Triangle.
The angle bisector, c o ―, divides ∠ a c b into two congruent angles. That line that was used to cut the angle in half is. But note that you never get similar triangles when you bisect an angle of a triangle (unless you.
Post a Comment for "Angle Bisector Theorem Definition"